09
2024
-
09
Engelie net new use! The latest research from Southern Medical University shows that SGLT2 inhibitors promote ketogenic and improve MASH by inhibiting CD8 T cell activation.
Author:
Accumulation of autoaggressive CD8 T cells contributes significantly to liver injury and inflammation during the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH).EMPA, a highly selective sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, has potential therapeutic effects on hepatic steatosis; however, the underlying mechanism has not been fully elucidated.
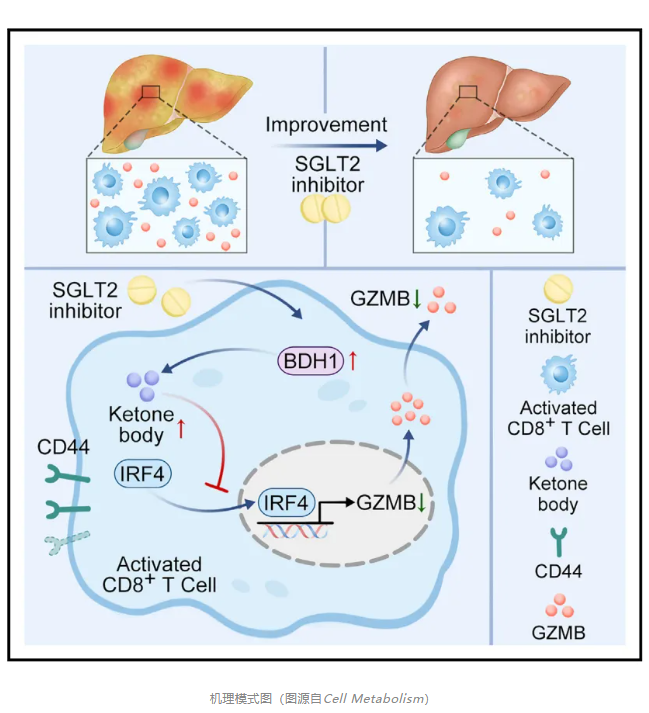
On September 6, 2024, Zhang Huijie, Yang Wei and Li Jin of Southern Medical University jointly communicatedCell Metabolism(IF=27.7)Published online entitled“SGLT2 inhibitor promote ketogenesis to improve MASH by suppressing CD8+T cell activation”The research paper,The study showedSGLT2 inhibitors inhibit CD8+T cell activation promotes ketogenesis and improves MASH.
Here, the researchers found that EMPA significantly reduced the autoinvasive CD8+Liver accumulation of T cells reduced granzyme B levels in MASH mice. Mechanically, EMPA increases 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase 1 (Bdh1), promote the expression of CD8+T-cell ketogenesis, which increases beta-hydroxybutyrate. β-hydroxybutyric acid subsequently inhibits interferon regulatory factor 4 (Irf4), this is CD8+Key to T cell activation. In addition, in T cellsBdh1Ablation of MASH aggravates the performance of MASH and hinders the therapeutic effect of EMPA. In addition, a case-control study also showed that SGLT2 inhibitor treatment inhibited CD8+T cell infiltration, improved liver injury in MASH patients.Taken together, the study suggests that SGLT2 inhibitors can target CD8+T cells, may be an effective strategy for the treatment of MASH.
Dysregulation of innate and adaptive immunity in the liver, followed by inflammation, has a key role in the development of MASH. In T-lymphocyte subsets, CD8+T cells and CD4+T cells are important contributors to adaptive immunity.CD8 T cells, especially cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), exert their effector function by releasing cytokines such as granzyme B (GZMB) and interferon gamma (IFN-γ), while CD4+T cells play a regulatory role in maintaining the function of other immune cell populations.Previous studies have shown that CD8+T cells, as pro-inflammatory cells, regulate the progression of MASH. In addition, CD8+T cells preferentially utilize non-glucose physiologic carbon sources as metabolic fuel, and their activation and effector functions are modulated by carbon availability Several studies have highlighted the potential of modulating ketone body metabolism as a promising means of modulating T cell activation and effects.
Chongqing Chongfan Technology Co., Ltd. Optical platform film thickness meter OCT optical coherence tomography LabVIEW control
LATEST NEWS
2024-09-16
Tsinghua University Xiao Bailong/Peking University Ouyang Kunfu Collaboration Reveals Key Phosphorylation Sites That Regulate Piezo1 Mechanical Sensitivity and Mechanotransduction Function in Vivo
Piezo1 is a mechanically activated cation channel that can convert mechanical forces into various physiological processes. Due to its large protein size of more than 2500 amino acids and complex 38 transmembrane helix topology, how Piezo1 is post-translationally modified to regulate its mechanotransduction function in vivo remains unexplored.
2024-09-18
Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wang Cong Yi/Sun Fei found in obese environment really pathogenic adipose tissue macrophage subsets
Adipose tissue macrophages (ATMs) play an important role in maintaining adipose tissue homeostasis and coordinating metabolic inflammation. Given the extensive functional heterogeneity and phenotypic plasticity of ATMs, there is a need to identify truly pathogenic subpopulations of ATMs in the context of obesity.
2024-09-14
Wang Su's team at Southeast University found that microenvironmental glial cells regulate stem cell self-renewal and differentiation by delivering iron to neural stem cells through ferritin
The study of neural stem cells is of great significance for the treatment of neural development and nervous system diseases. However, the regulation mechanism of neural stem cells has not been fully elucidated, especially the regulation of neural stem cells by microenvironment is relatively less known.
2024-09-14
Subversion of the past! Tsinghua University Dai Qionghai/Guo Zengcai/Wu Jiamin Cooperation Latest Cell
A comprehensive understanding of physiopathological processes requires non-invasive live three-dimensional (3D) imaging on different spatial and temporal scales. However, huge data throughput, optical non-uniformity, surface irregularities, and phototoxicity pose huge challenges, resulting in inevitable trade-offs between volume size, resolution, speed, sample health, and system complexity.
2024-09-11
The latest research by Guo Jianping/Cheng Chao/Bo Lang of Sun Yat-sen University confirms that palmitic acid can suppress virus infection by activating innate immunity!
Innate immunity is the primary defense against viral and microbial infections. The exact effect of cellular metabolites, particularly fatty acids, on antiviral innate immunity remains largely elusive.

