23
2025
-
06
Relationship between the asymmetric shape of metamaterial metasurface and the Q value in q-BICs
Author:
Symmetry-protected bound states in the continuum (SP-BICs) are a type of bound state in the continuum that can be transformed into quasi-BICs by breaking the structural symmetry. Quasi-BICs have finite but still very high quality factors (Q-factors).
There is also a lot of work on breaking the structural symmetry to convert BICs to quasi-BICs; however, The relationship between the asymmetry parameter and the Q-value of quasi-BICs under different types of symmetry breaking schemes remains to be explored. 。
A recent article titled " Engineering High Quality Quasi-Bound States in the Continuum Through Controlled Symmetry Breaking in All-Dielectric Metasurfaces " published in Laser & Photonics Reviews indicates that the relationship between the Q-value and the asymmetry parameter of the metasurface structure can be explained by the perturbation theory of eigenfields. This research result comes from the research team of Professor Lujun Huang at East China Normal University.
This work also uses the proposed idea to design structures with Q-factors greater than, which is of great significance for guiding the design of high-Q metasurfaces.
The article studies the asymmetric metasurface structures of eccentric holes, U-shaped structures, and L-shaped structures, and uses formula fitting to evaluate the relationship between the Q-value and the asymmetry parameter of the structure. The study found that both the intercept and slope in the fitting curve can be controlled by these asymmetry parameters.
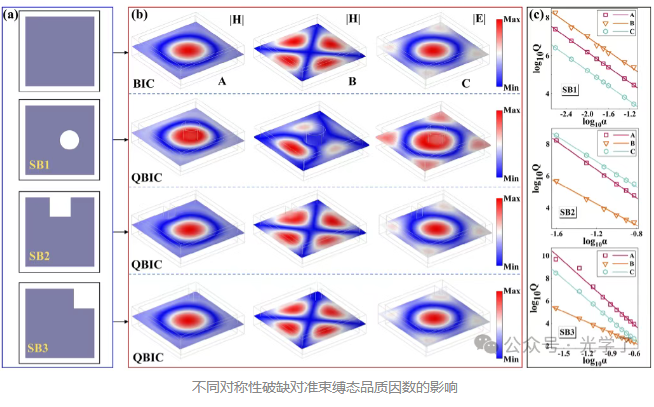
The article conducts numerical calculations and experiments on the three structures mentioned above. The modal field, multipolar scattering decomposition, and Q-value parameters of the structure are analyzed to prove the control conversion of the structure from symmetry-protected bound states to quasi-bound states by the proposed asymmetry parameters.
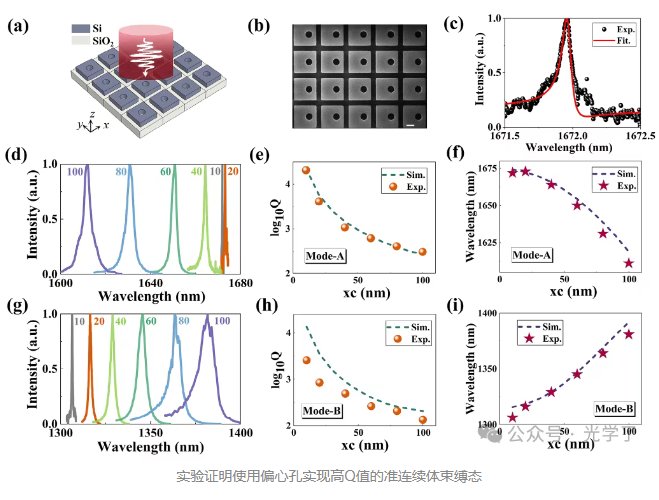
The article systematically studies the influence of symmetry breaking on the quality factor of quasi-bound states supported by all-dielectric metasurfaces composed of rectangular silicon nanopillar arrays. Three symmetry breaking methods are used to convert symmetry-protected bound states into quasi-bound states with customized Q values.
The results show that the fundamental reason for the difference in Q values is the perturbation of the eigenfield caused by different structures. For metasurfaces with eccentric cylindrical air holes, Q value optimization shows a dual dependence on the air hole radius and the direction of movement. Notably, by precisely controlling the air hole radius, the hierarchical order of resonance modes (the hierarchical arrangement of Q value sizes) can be reconfigured. Unlike this radial perturbation scheme, symmetry breaking achieved through U-shaped and L-shaped geometric modifications produces the opposite Q value hierarchy: Mode B consistently exhibits the lowest Q value in both structures, while Mode A (L-shaped) and Mode E (U-shaped) exhibit Q value enhancement, respectively.
Experimental verification using devices with controllable symmetry breaking parameters fabricated by nanofabrication confirms the theoretical predictions, and the results of reflectance spectral measurements are highly consistent with numerical simulations. The optimized structure achieves excellent resonance quality, with Q values consistently exceeding 10000, and the peak Q value measured experimentally reaches 30270. This systematic exploration establishes a reasonable design framework for designing ultra-high-Q metasurface resonators through symmetry control, providing a key perspective for photonic applications requiring enhanced extreme light-matter interaction.
LATEST NEWS
2025-07-12
Hyperspectral channel density on-chip diffractive speckle spectrometer
Driven by the demand for high-performance miniature spectrometers, research on chip-scale spectrometers is continuously breaking through towards high integration, high resolution, and large bandwidth. This work proposes a silicon-based on-chip spectrometer based on cascaded disordered metasurfaces. Through various on-chip wavefront modulation mechanisms, high-spectral speckle is generated, which expands the number of spectral channels with a compact chip size, thus achieving extremely high on-chip spectral channel density and providing an effective means for achieving high-resolution, large-bandwidth spectral detection.
2025-07-14
Ultrasensitive room-temperature extreme photoelectric response achieved
This study, for the first time, achieved the control of ultra-sensitive photoelectric response optimized for room temperature conditions through electromagnetically induced potential well effects and exciton insulator phase transition characteristics.
2025-07-15
Preparation and research progress of glass scintillators for X-ray imaging
Developing suitable host materials with strong X-ray absorption coefficient, good exciton transport efficiency, low phonon energy, and high lanthanide ion solubility remains a cutting-edge research direction in the field of X-ray detection.
2025-07-16
Quantum logic gates based on single-piece gradient metasurface
In today's rapidly developing quantum information technology, realizing efficient and highly integrated quantum logic gates is one of the key challenges in the field of integrated quantum optics.
2025-07-17
Preparation and performance study of epoxy-thiol high-contrast color polymer dispersed liquid crystals
Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal (PDLC) is a smart material consisting of micron-sized liquid crystal droplets dispersed in a polymer matrix.

