26
2024
-
12
Analysis of Patent Trends for Quantum Dot Photodetectors
Author:
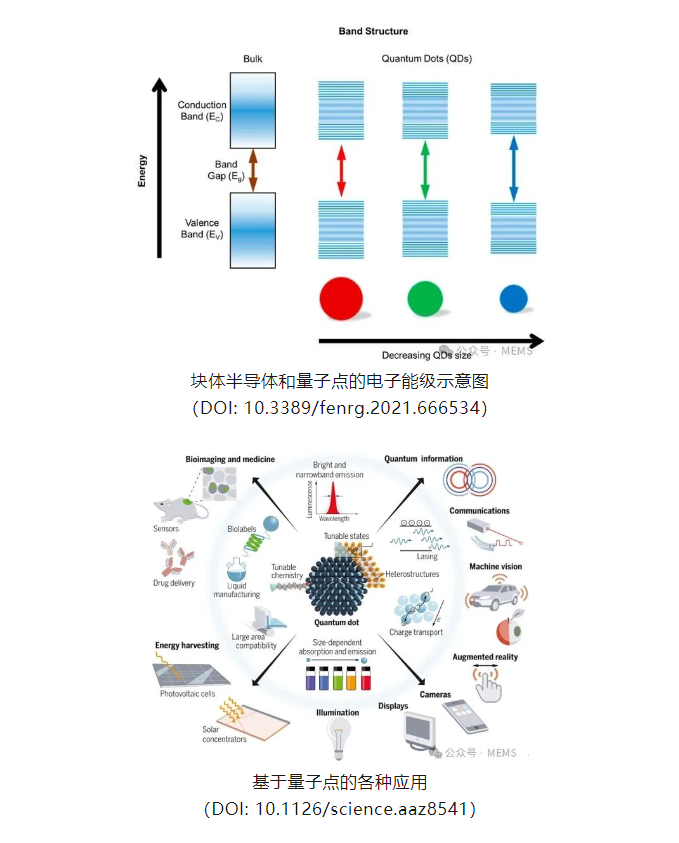
According to Memes Consulting, quantum dots (QDs) are also known as semiconductor nanocrystals, a quasi-zero-dimensional semiconductor nanostructure (spherical or quasi-spherical) with size-tunable properties, typically ranging from 2 to 20 nanometers in diameter. Due to their nanoscale size, the electrons and holes in quantum dots are quantum confined, transforming the continuous band structure into discrete energy levels with molecular characteristics, and their bandgap increases as the size decreases, allowing quantum dots to exhibit excellent tunable properties (including optical, photothermal, thermoelectric, optoelectronic, and electrical characteristics). In 2023, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Moungi G. Bawendi, Louis E. Brus, and Aleksey Yekimov for their outstanding contributions to the 'discovery and synthesis of quantum dots.' The pioneering work of these three scientists has laid a solid foundation for the development of quantum dot technology and facilitated its transition from laboratory research to practical applications. Today, quantum dots are widely used in fields such as display and lighting, sensing and imaging, energy collection and storage, as well as biological labeling and analysis.
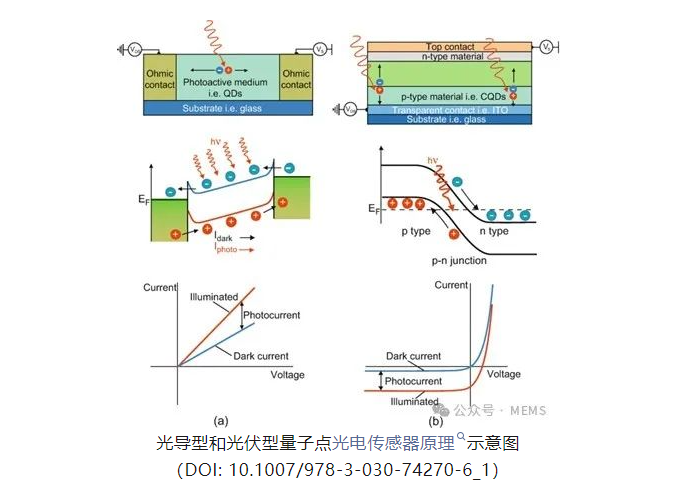
Quantum dot photodetectors are devices that utilize the optoelectronic properties of quantum dot materials to convert optical signals into usable electrical signals. Based on the principle of photoelectric conversion, they can be mainly divided into two categories: photoconductive and photovoltaic. Additionally, there is a trapping mode that combines the above two types.
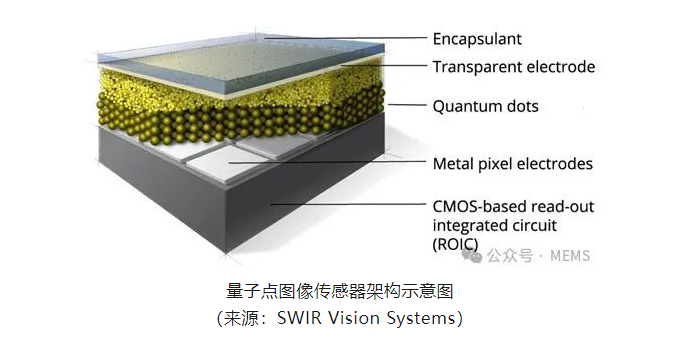
The architecture of quantum dot image sensors is similar to that of back-illuminated (BSI) CMOS image sensors. A thin film made of quantum dot materials replaces silicon as the photosensitive layer integrated above the readout circuit (ROIC) through printing or spin-coating processes. This design is easy to scale up for mass production and features wide spectral response, wide dynamic range, thin design, and support for electronic global shuttering, showing great market application prospects.
According to Memes Consulting, in recent years, technology giants represented by Apple, Samsung Electronics, STMicroelectronics, and startups like SWIR Vision Systems, Emberion, Qurv, Quantum Solutions, and SMIC Thermal have been competing to develop related technologies and patent layouts. This is driving breakthroughs in quantum dot photodetector technology and the commercialization of products, especially in sensing and imaging in the short-wave infrared (SWIR) band. In 2017, Apple acquired Invisage Technologies, which focuses on developing quantum dot image sensor technology, aiming to integrate quantum dot technology into its product ecosystem and strengthen its technological reserves in high-end imaging. In 2018, SWIR Vision Systems (acquired by onsemi in July 2024) released the first 2.1-megapixel CQD® SWIR camera, marking the entry of quantum dot photodetectors into the commercialization stage. In 2021, STMicroelectronics showcased a colloidal quantum dot global shutter SWIR image sensor with a pixel pitch of 1.62 μm at the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), which was fabricated in its own 12-inch wafer fab and is expected to be mass-produced at relatively low costs. In 2022, SMIC Thermal collaborated with Professor Tang Xin's team from Beijing Institute of Technology to develop the first short-wave infrared and mid-wave infrared imaging chips with cutoff wavelengths reaching 2.5 μm and 5 μm respectively and achieved wafer-level fabrication processes for 4-8 inches. In 2024, Emberion launched a new ultra-low-cost SWIR quantum dot image sensor that reduced its mass production cost to €50 and plans to launch its first product based on this ultra-low-cost quantum dot image sensor in 2025. As companies like STMicroelectronics and Emberion successively introduce low-cost mass-produced quantum dot image sensors, this technology is expected to accelerate its adoption in mass markets such as automotive electronics and consumer electronics, potentially bringing innovation and transformation to more industries.

As the global quantum dot photodetector industry flourishes, it is essential to understand the patent layout and status of manufacturers and research institutions in this field while identifying new entrants in the quantum dot photodetector sector and the threats they may pose. In this report, Memes Consulting conducts an in-depth analysis of the current status and trends of global and Chinese patents related to quantum dot photodetectors. It identifies leading manufacturers, new entrants, and research institutions in this field while statistically analyzing their patent application activities related to quantum dot photodetectors. This provides valuable reference material for professionals engaged in technology research, product innovation, and industry-academia collaboration.
Overview of global patent applications for quantum dot photodetectors
According to statistics and analysis by Memes Consulting, there have been over 1,600 cumulative patent applications for quantum dot photodetectors globally involving more than 300 patent applicants. From the trend of global patent applications for quantum dot photodetectors: from 1991 to 2003 was a budding period with fewer than ten applications per year; from 2004 to 2014 was an oscillating development period where annual applications grew from 13 to 66; from 2015 onwards has been a stable development period with annual applications maintaining above 120. It should be noted that apart from patent applications that require early publication, patent applications are usually published after being filed for 18 months; therefore applications from 2023 and 2024 may not yet be fully disclosed; data statistics are for reference only.

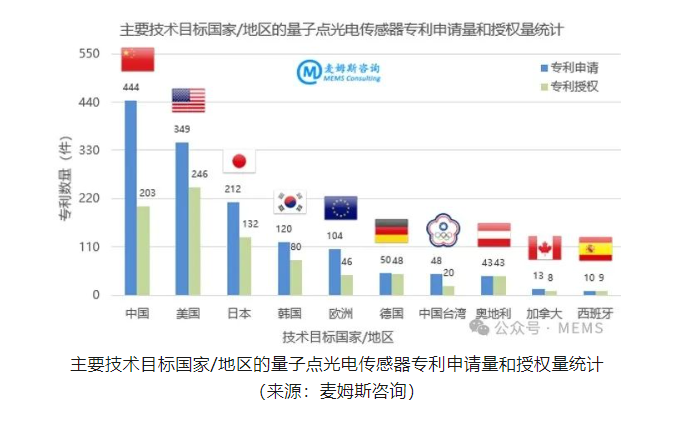
Patent applications for quantum dot photodetectors are mainly concentrated in China (excluding Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan), the United States, Japan, South Korea, Europe, Germany among other countries/regions. Among them, there are 444 patent applications for quantum dot photodetectors filed in China leading the way; the top five countries/regions by granted patents for quantum dot photodetectors are respectively: United States (246), China (203), Japan (132), South Korea (80), Germany (48).
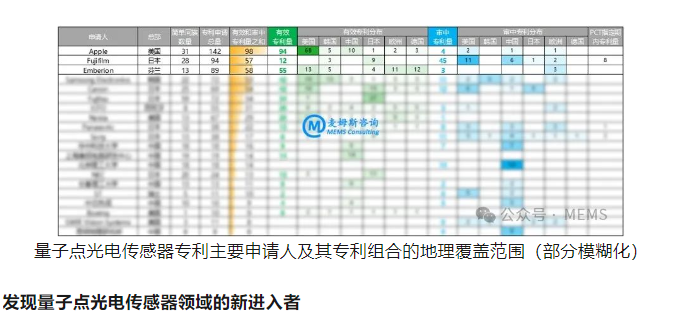
Patent applications can reflect a country or applicant's investment level in specific technology development while providing clues about major applicants' technological maturity. This report statistically analyzes over 1,600 patents related to quantum dot photodetectors; Memes Consulting presents a ranking of the top twenty applicants by effective patents and those under examination in the following chart (based on the sum of effective patents and those under examination). Overall view shows that Apple, Fujifilm, Emberion, Samsung Electronics, Canon rank high in total patent applications as well as effective patents plus those under examination indicating strong R&D capabilities with a focus on global patent layouts. Additionally Fujitsu with many effective patents along with ICFO (Institute of Photonic Sciences) from Spain and Nokia also demonstrate strong technological innovation capabilities; institutions like Beijing Institute of Technology with many patents under examination along with Sony and Panasonic also show significant technological innovation capabilities.
Discovering new entrants in the field of quantum dot photodetectors
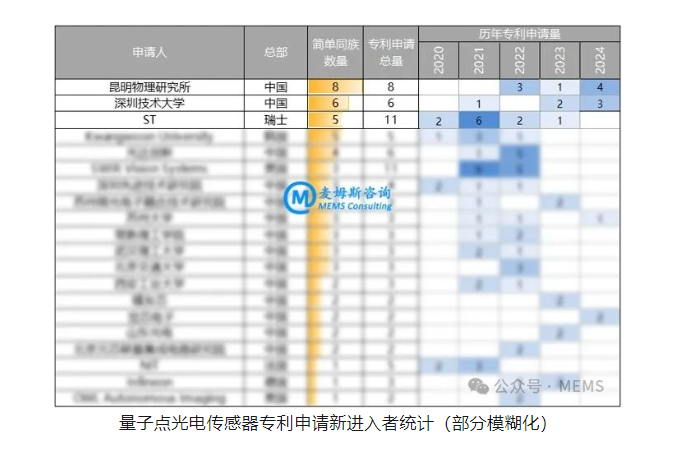
New entrants in the patent application for quantum dot photodetectors refer to applicants who first applied for patents in this field from 2020 to 2024. MEMS Consulting provided a ranking of the top 20 new entrants based on the number of simple families. Among them, the Kunming Institute of Physics has a simple family count of 8, ranking first; Shenzhen Technology University, STMicroelectronics, Kwangwoon University, and Guangda Innovation have simple family counts of 6, 5, 5, and 4 respectively, ranking second to fifth. Among these 20 new entrants, the number of applicants from China, the United States, Switzerland, South Korea, Germany, and France are 14, 2, 1, 1, 1, and 1 respectively. The proportion of Chinese applicants reaches 70%, indicating that China is actively laying out in the field of quantum dot photodetectors to accelerate its development process.
Competitive landscape and patent layout strategy of major applicants
This report clearly presents active patent applicants in the field of quantum dot photodetectors. Through an analysis of the patent portfolios of major patent applicants, it reveals their intellectual property status. The report provides an in-depth analysis of the patent portfolios of 10 leading manufacturers, 8 new entrants, and 10 leading research institutions in quantum dot photodetectors, introducing their patent application overview, application activity level, key patents, and recently applied patents. Additionally, the analysis of patent transfers reveals manufacturers that have entered this field through acquisitions.
Quantum dot photodetector patent database
MEMS Consulting also provides an Excel database containing all quantum dot photodetector patents analyzed in this report, supporting multi-field retrieval including publication number, title, application date, priority date, publication (announcement) date, authorization date, estimated expiration date, current applicant (patent holder), current applicant (patent holder) address, original applicant (patent holder), original applicant (patent holder) address, inventor, legal status/event, receiving office, IPC classification number, citation count, number of simple family members, total citation count for simple families, etc.
Chongqing Chongfan Technology Co., Ltd. Optical platform Film thickness gauge OCT Optical coherence tomography LabVIEW control
LATEST NEWS
2025-01-09
Design and Development of Full-Spectrum Photodetectors
In recent years, the booming optoelectronic industry has changed the world and extended into many aspects of life. Among them, photodetectors (PDs) with a wide response bandwidth from deep ultraviolet to visible to near-infrared serve as important optoelectronic components and play a key role in daily life.
2025-01-08
Black arsenene multi-spectral integrated field-effect transistors, aiding high-resolution imaging and enhanced secure communication.
With the development of modern communication technology, the demand for broadband, room-temperature infrared, and terahertz (THz) detectors has rapidly increased. These detectors play a crucial role in fields such as telecommunications, security inspection, non-destructive testing, and medical diagnostics. However, existing optical detectors face challenges such as high intrinsic dark current and the need for low-temperature cooling, which limit their efficiency in detecting low-energy photons. Particularly in the terahertz band, the photon energy is insufficient to excite electron transitions from the valence band maximum (VBM) to the conduction band minimum (CBM), making effective optoelectronic conversion difficult. Therefore, researchers have been seeking ultra-broadband detectors that can operate at room temperature and respond to wavelengths ranging from visible light to the terahertz band.
2024-12-30
Laser-based tiered neurons achieve high-speed reservoir computing.
Neuromorphic computing is a computational paradigm that simulates the functions and architecture of biological neurons. A single biological neuron is a powerful computational unit with information processing capabilities, information transmission abilities, and memory functions. Therefore, it is crucial to design a photonic neuromorphic processor that can truly emulate the powerful computational functions of biological neurons.
2025-01-01
Design and Development of Full-Spectrum Photodetectors
In recent years, the rapidly growing optoelectronic industry has changed the world and extended into many aspects of life. Among them, photodetectors (PDs) with a wide spectral response from deep ultraviolet to visible to near-infrared serve as important optoelectronic components and play a key role in daily life.
2024-12-31
High-sensitivity quantum dot photodetectors from deep ultraviolet to near-infrared
In recent years, the rapidly growing optoelectronic industry has changed the world and extended into many aspects of life. Among them, photodetectors (PD) with deep ultraviolet-visible-near infrared full spectrum detection response serve as important optoelectronic components, playing a key role in daily life.

