13
2024
-
12
Wide-band Nb₃Se₁₂I photodetector, aiding ultra-wideband detection and encrypted imaging applications
Author:
With the development of the digital age, the demand for enhanced information transmission and storage technologies has been growing explosively, and information security is receiving increasing attention. Photons, as the fundamental carriers of information, play an indispensable role in information transmission and processing due to their characteristics of high speed, low energy consumption, and large capacity. Compared to pure spectral detection and imaging, the multiple degrees of freedom in the cooperative engineering of photons in ultra-wideband systems provide unprecedented information capacity, opening up opportunities for applications in all-weather monitoring, low-light visibility enhancement, secure imaging, and advanced biomedical diagnostics.
Traditional imaging sensors are made of silicon-based charge-coupled devices, which cannot detect light with wavelengths exceeding 1100 nm. To extend the detection range beyond this limit, other semiconductor materials with narrower bandgaps (such as InxGa1-xAs and Hg1-xCdxTe) are used to manufacture photon-type photodetectors. However, detecting long-wavelength light requires strict low-temperature cooling conditions to minimize thermal excitation noise and dark current, and photodetectors operating in the mid-wave infrared (especially terahertz) region are bulky and consume a lot of power, leading to significant drawbacks. Additionally, traditional photon-type detectors based on photoconductive and photogating effects typically require a bias voltage to be applied to the channel, resulting in excess noise that affects performance. Photothermal electric (PTE) devices are not limited by material bandgaps, thus having the capability to collect light over a wide spectrum at any specific wavelength. Polarization information is another important optical parameter independent of phase and amplitude, and the encryption of polarization information has strong concealment, fundamentally avoiding illegal interception and tampering of information. Therefore, finding materials that possess both thermoelectric properties and sensitivity to polarized light is crucial for the development of new detection and encryption technologies.
According to MEMS Consulting, Professor Yang Rusen's research team at Xi'an University of Electronic Science and Technology has controllably synthesized quasi-one-dimensional material Nb₃Se₁₂I using chemical vapor transport methods. Based on the photothermal electric and photoconductive synergistic effects of this material, the fabricated photodetector can cover a wide spectral response range from deep ultraviolet (254 nm) to terahertz (0.30 THz) and has fast and accurate wide-spectrum imaging capabilities. This detector also demonstrates excellent multiple synergistic effects and high responsiveness, providing an effective new strategy for high-capacity optical processing. The related research results were published under the title '1D Alloy Nb3Se12I Based Photodetector for Ultrabroadband Light-Detection and Encryption Imaging Application' inAdvanced Materialsjournal.
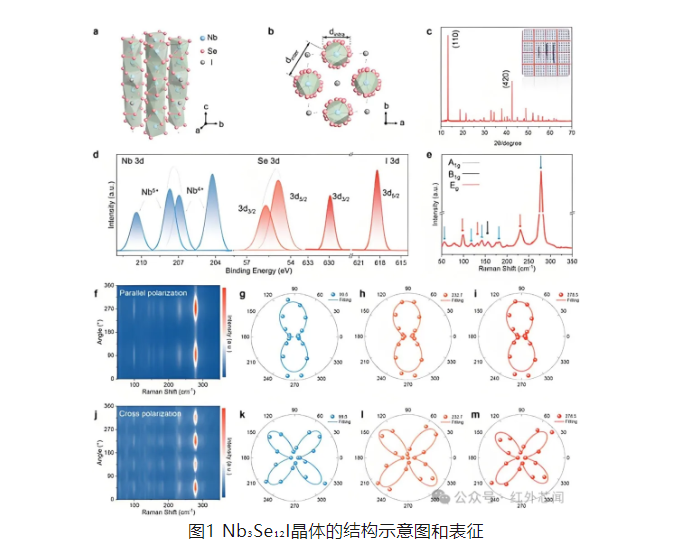
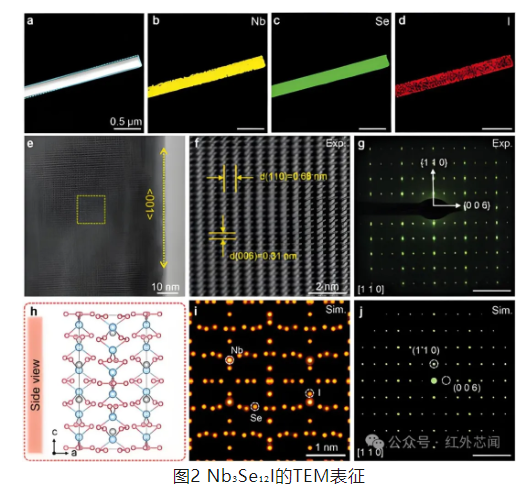
Figure 1a shows the tetragonal structure of Nb₃Se₁₂I crystals, and Figure 1d reveals the chemical composition and elemental presence of the crystals using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis. Subsequently, the researchers further characterized the crystal structure of the exfoliated samples using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), with the relevant results shown in Figure 2.
To study the optical response characteristics of the Nb₃Se₁₂I photodetector, the researchers conducted electrical and optoelectronic measurements, with the relevant measurement results shown in Figure 3. Figure 3a presents a schematic diagram of the Nb₃Se₁₂I photodetector. Additionally, the researchers compared the working wavelength and responsivity of Nb₃Se₁₂I with other quasi-one-dimensional materials, with the results shown in Figure 3e. The response mechanisms of the Nb₃Se₁₂I device across a wide spectrum are summarized as follows: The response mechanism of the Nb₃Se₁₂I detector in the deep ultraviolet band is the photoconductive effect, the response mechanism in the 405 nm to 2200 nm band is the photothermal electric synergistic photoconductive effect, and the response mechanism at a wavelength of 4060 nm is the photothermal electric effect.
LATEST NEWS
2025-01-09
Design and Development of Full-Spectrum Photodetectors
In recent years, the booming optoelectronic industry has changed the world and extended into many aspects of life. Among them, photodetectors (PDs) with a wide response bandwidth from deep ultraviolet to visible to near-infrared serve as important optoelectronic components and play a key role in daily life.
2025-01-08
Black arsenene multi-spectral integrated field-effect transistors, aiding high-resolution imaging and enhanced secure communication.
With the development of modern communication technology, the demand for broadband, room-temperature infrared, and terahertz (THz) detectors has rapidly increased. These detectors play a crucial role in fields such as telecommunications, security inspection, non-destructive testing, and medical diagnostics. However, existing optical detectors face challenges such as high intrinsic dark current and the need for low-temperature cooling, which limit their efficiency in detecting low-energy photons. Particularly in the terahertz band, the photon energy is insufficient to excite electron transitions from the valence band maximum (VBM) to the conduction band minimum (CBM), making effective optoelectronic conversion difficult. Therefore, researchers have been seeking ultra-broadband detectors that can operate at room temperature and respond to wavelengths ranging from visible light to the terahertz band.
2024-12-30
Laser-based tiered neurons achieve high-speed reservoir computing.
Neuromorphic computing is a computational paradigm that simulates the functions and architecture of biological neurons. A single biological neuron is a powerful computational unit with information processing capabilities, information transmission abilities, and memory functions. Therefore, it is crucial to design a photonic neuromorphic processor that can truly emulate the powerful computational functions of biological neurons.
2025-01-01
Design and Development of Full-Spectrum Photodetectors
In recent years, the rapidly growing optoelectronic industry has changed the world and extended into many aspects of life. Among them, photodetectors (PDs) with a wide spectral response from deep ultraviolet to visible to near-infrared serve as important optoelectronic components and play a key role in daily life.
2024-12-31
High-sensitivity quantum dot photodetectors from deep ultraviolet to near-infrared
In recent years, the rapidly growing optoelectronic industry has changed the world and extended into many aspects of life. Among them, photodetectors (PD) with deep ultraviolet-visible-near infrared full spectrum detection response serve as important optoelectronic components, playing a key role in daily life.

