04
2024
-
12
Thermochromic micro-patterned hydrogels: Breaking through the challenge of compatibility between rapid invisibility and intelligent light control.
Author:
Currently, about 15% of global electricity is used forneutralizationtemperature rise caused by solar heatingto create a comfortable working temperature environment.Hydrogel with thermochromic properties can automatically adjust its transmission characteristics to the solar spectrum with temperature changes, achieving intelligent solar thermal regulation, which has great application potential in energy saving. However, thermochromic hydrogels can only regulate their transmission characteristics to the solar spectrum through temperature (thermal) stimulation, thus only exhibiting their visible light stealth (VLS) capability under high-temperature conditions. In addition, the response time of VLS can be as long as 180 seconds. During such a slow response process, sensitive information hidden by the thermochromic hydrogel may have already been leaked, indicating that thermochromic hydrogels cannot meet the rapid stealth needs for military (camouflage) and civilian (privacy protection) applications.Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop a new technology that can simultaneously achieve rapid visible light stealth and intelligent solar thermal regulation to meet the dual-use needs of military and civilian applications.
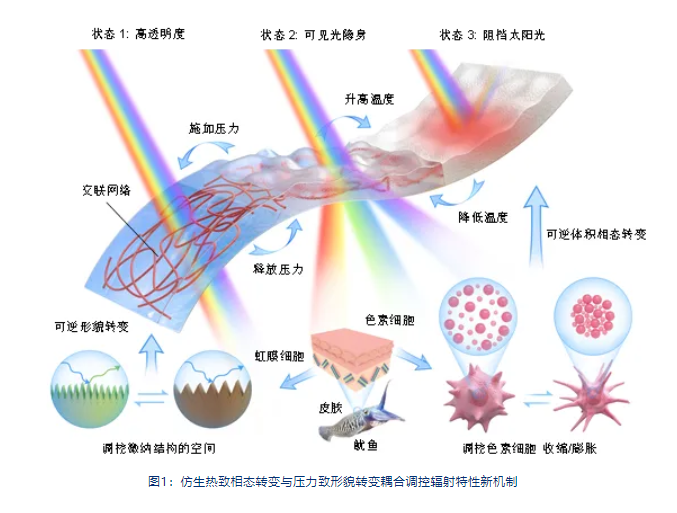
A new mechanism for regulating radiation characteristics through bionic thermally induced phase transition and mechanically induced morphological transition has been established.
Drawing on the color-changing mechanism of squid skin, a bionic micro-patterned thermochromic hydrogel (MTH) has been proposed. This MTH utilizes the coupling effect of thermally induced phase transition and mechanically induced morphological transition to achieve regulation of its radiation characteristics in all dimensions (frequency, space, and angle), establishing a new mechanism for regulating radiation characteristics.
Theregulation mechanism of MTH's radiation characteristicsis shown inFigure 1.On one hand, the thermochromic hydrogel relies on its special optical properties. Under high temperature (thermal stress) stimulation, the aggregation of molecular chains within the hydrogel causes it to change from a colorless transparent state to a white opaque state, thereby blocking sunlight. Moreover, this phase transition is reversible; when the high-temperature stimulus is removed, the internal molecules form good interactions with water molecules through hydrogen bonds, allowing the hydrogel to return to a colorless transparent state. This temperature-adaptive color-changing mechanism draws well from the color-changing mechanism of pigment cells in squid skin, endowing MTH with intelligent photothermal regulation capabilities. On the other hand, under pressure stimulation, the surface morphology of MTH undergoes a reversible morphological transition, allowing MTH to switch freely between direct transmission and diffuse transmission of visible light. This pressure-regulated mechanism of MTH's radiation characteristics endows MTH with rapid VLS capability, reducing the VLS response time from the traditional 180 seconds to within 1 second.
Low-cost, simple template method endows MTH with potential for large-scale application.
Using low-cost and suitable flexible sandpaper as a template for large-scale production, MTH of different sizes has been successfully prepared. The preparation process of MTH is shown inFigure 2.By adding a layer of flexible sandpaper on a double-layer glass plate, an MTH mold can be made. The hydrogel precursor solution is added to the mold for gelation, and then the sandpaper template is peeled off to obtain the final MTH. This method is not only simple and efficient but also low-cost, enabling large-area production and greatly enhancing the scalability of MTH applications. The final prepared MTH of different sizes is displayed inFigure 3..


LATEST NEWS
2025-01-09
Design and Development of Full-Spectrum Photodetectors
In recent years, the booming optoelectronic industry has changed the world and extended into many aspects of life. Among them, photodetectors (PDs) with a wide response bandwidth from deep ultraviolet to visible to near-infrared serve as important optoelectronic components and play a key role in daily life.
2025-01-08
Black arsenene multi-spectral integrated field-effect transistors, aiding high-resolution imaging and enhanced secure communication.
With the development of modern communication technology, the demand for broadband, room-temperature infrared, and terahertz (THz) detectors has rapidly increased. These detectors play a crucial role in fields such as telecommunications, security inspection, non-destructive testing, and medical diagnostics. However, existing optical detectors face challenges such as high intrinsic dark current and the need for low-temperature cooling, which limit their efficiency in detecting low-energy photons. Particularly in the terahertz band, the photon energy is insufficient to excite electron transitions from the valence band maximum (VBM) to the conduction band minimum (CBM), making effective optoelectronic conversion difficult. Therefore, researchers have been seeking ultra-broadband detectors that can operate at room temperature and respond to wavelengths ranging from visible light to the terahertz band.
2024-12-30
Laser-based tiered neurons achieve high-speed reservoir computing.
Neuromorphic computing is a computational paradigm that simulates the functions and architecture of biological neurons. A single biological neuron is a powerful computational unit with information processing capabilities, information transmission abilities, and memory functions. Therefore, it is crucial to design a photonic neuromorphic processor that can truly emulate the powerful computational functions of biological neurons.
2025-01-01
Design and Development of Full-Spectrum Photodetectors
In recent years, the rapidly growing optoelectronic industry has changed the world and extended into many aspects of life. Among them, photodetectors (PDs) with a wide spectral response from deep ultraviolet to visible to near-infrared serve as important optoelectronic components and play a key role in daily life.
2024-12-31
High-sensitivity quantum dot photodetectors from deep ultraviolet to near-infrared
In recent years, the rapidly growing optoelectronic industry has changed the world and extended into many aspects of life. Among them, photodetectors (PD) with deep ultraviolet-visible-near infrared full spectrum detection response serve as important optoelectronic components, playing a key role in daily life.

