23
2025
-
05
Multicolor and polarization photodetectors based on heterojunctions, aiding polarization imaging and optical communication applications
Author:
α-In₂Se₃ exhibits planar anisotropic photoresponse characteristics, while 2H-MoTe₂ possesses broadband optical absorption in the near-infrared band. The combination of these two enables the heterostructure to achieve multicolor and polarization-sensitive photodetection. In the experiment, 2D α-In₂Se₃ and 2H-MoTe₂ nanosheets were prepared by mechanical exfoliation and manually stacked to form a van der Waals heterostructure. Figure 1 shows the structure and characterization of the α-In₂Se₃/2H-MoTe₂ van der Waals heterostructure.
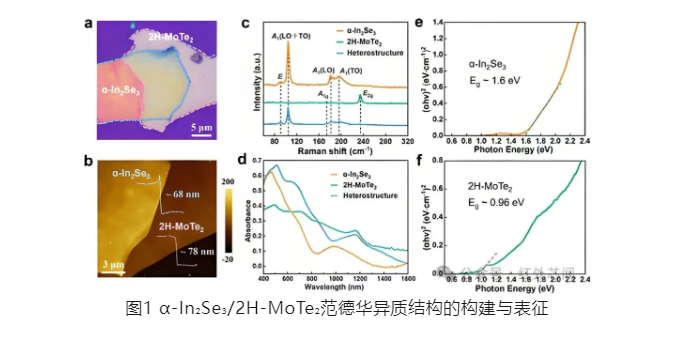
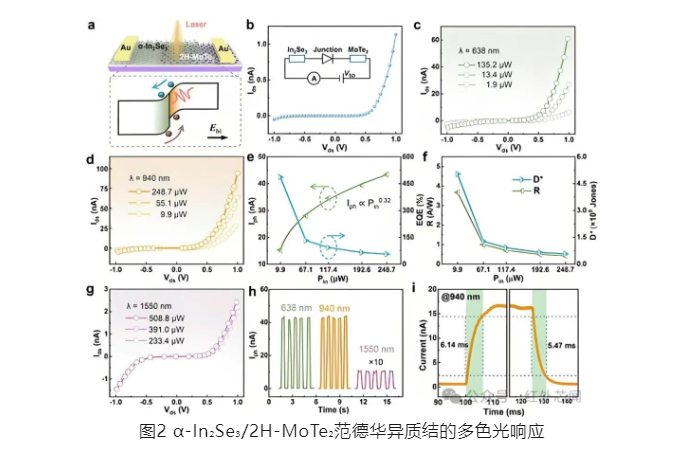
Subsequently, researchers determined the work functions of α-In₂Se₃ and 2H-MoTe₂ to be 4.62 eV and 4.68 eV, respectively, using ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS). Based on this, it was calculated that a type-II band alignment formed at the heterojunction interface. The heterostructure exhibited broadband optical absorption characteristics in the visible to near-infrared spectral range, and achieved efficient photodetection performance at a wavelength of 940 nm. The relevant research results are shown in Figure 2.
Researchers further investigated the photoresponse mechanism of the device using a scanning photocurrent microscope at 638 nm, 940 nm, and 1550 nm, with relevant results shown in Figure 3. The results indicate that at 638 nm and 940 nm wavelengths, photogenerated carriers are effectively separated in the heterojunction region, while at 1550 nm, the photoresponse is relatively weak due to weaker absorption. Furthermore, the heterostructure exhibits polarization-sensitive characteristics at 638 nm and 1550 nm wavelengths, with polarization ratios of 1.40 and 1.07, respectively. The relevant results are shown in Figure 4.
To verify the polarization imaging and optical communication capabilities of this heterostructure photodetector, researchers conducted polarization imaging and ASCII code transmission experiments, respectively. The relevant experimental setup and results are shown in Figure 5. Experimental results show that the detector can achieve high-resolution polarization imaging and accurately receive and decode optical signals, demonstrating its application potential in the fields of imaging and optical communication.
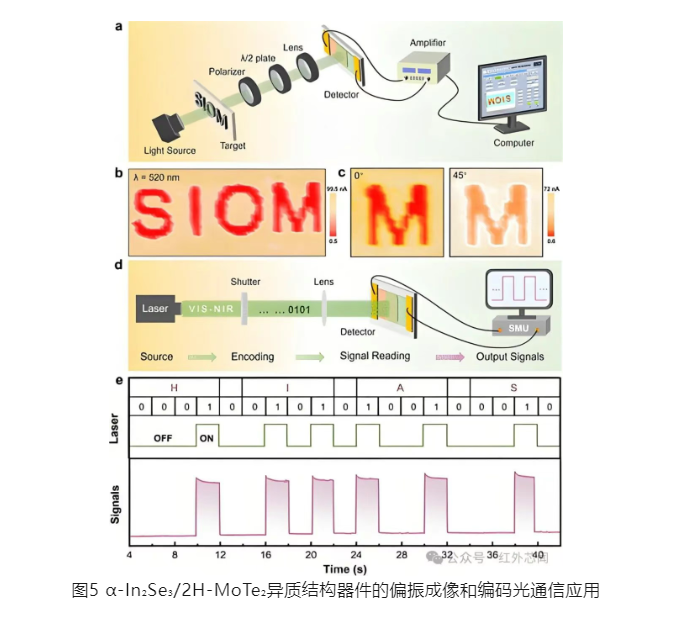
In summary, this research achieved multicolor and polarization-sensitive photodetection by constructing an α-In₂Se₃/2H-MoTe₂ van der Waals heterostructure, exhibiting excellent photodetection performance at a wavelength of 940 nm. The heterostructure demonstrates polarization-sensitive characteristics at 638 nm and 1550 nm wavelengths, enabling high-resolution polarization imaging and optical communication. By utilizing the intrinsic material properties and external field modulation capabilities of van der Waals heterostructures, a promising solution is provided for the next generation of high-performance multifunctional photodetectors.
Previous
Previous

